What are Motherboard Drivers?
This article describes the purpose and importance of installing motherboard drivers to enable your system board to function properly and allow all system components (e.g. CPU, Memory modules, etc.) to work effectively.
This article describes the purpose and importance of installing motherboard drivers to enable your system board to function properly and allow all system components (e.g. CPU, Memory modules, etc.) to work effectively.
This articles provides valuable information on system drivers, device drivers integral to the operation of major system components of your computer (such as USB ports, Firewire, board chipsets, etc.). Solve Network, Bluetooth and drive problems with updated system drivers.
When you use a digital media device, you need to be able to load your favorite music and video on it. For the Microsoft Zune device, you use the Zune 3.0 software. But if the device is not recognized by your computer, the Zune software will not do anything. Troubleshoot Zune device errors to fix them.
Troubleshooting and solving computer errors is never fun, especially if serious Windows errors occur. Stop error 0x000000EA is an example of a serious error, which leads to the Windows blue screen of death. This specific stop error is a video card related error, which can often be solved following these steps…
All computer hardware needs device drivers to communicate with the operating system. In Windows, quite a few device drivers are included with the installation. But for a lot of hardware, special device drivers are required. If drivers are corrupted or not installed properly, Windows will report a device error. One of the device errors that the Windows Device Manager can report is a code 28 error.
The error message will be “The drivers for this device are not installed. (Code 28)”.
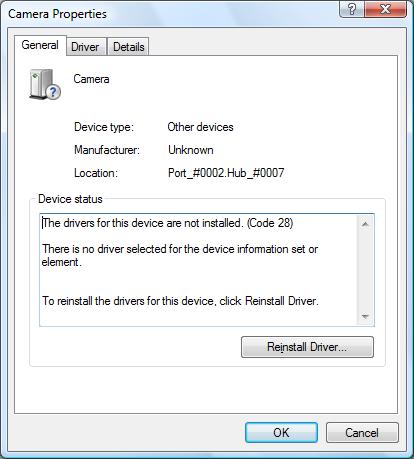
A code 28 error means that there is no driver installed for the hardware device. Most likely Windows does not have a default driver for the device, or it would be installed. This means that a special driver from the hardware manufacturer is required. The code 28 error can occur for any type of device, USB devices, audio devices, video devices, etc. In general, however, the error will occur for the more exotic hardware since Windows already supports quite a few common devices by default.
To fix code 28 errors, it is required to install the drivers for the device that is causing the code 28 error. You can use the device manager to update the drivers. Select the device in error, right-click the device, and in the pop-up menu select Update Driver Software (in newer Windows versions, the link is named Update driver). Windows will ask you for the location to install the drivers from, so make sure you download the drivers for the device from the hardware manufacturer’s website first and select the local folder where you saved the download drivers for the update.
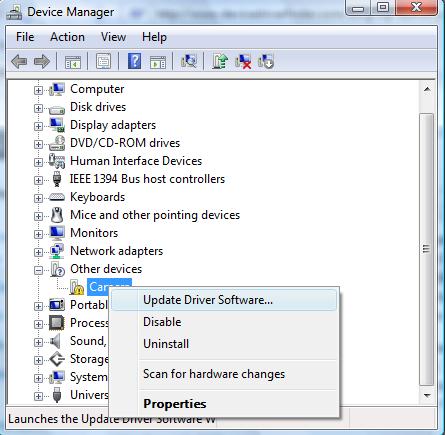
If you can not find the drivers for the device in error or are not comfortable with using the Windows Device Manager, you can also use a driver update tool to find, download and update all device drivers for you. A driver update program will accurately identify your hardware, including the device in error, and automatically install the latest drivers for it. This will solve code 28 errors.
It is also recommended to have Windows configured for automatic updates. This will ensure that any new drivers that are supported by Microsoft will automatically install or get updated so that your computer will be compatible with as many devices and hardware as possible.
Device drivers are required to allow operating systems to communicate with computer hardware. In each new version of Windows more and more device drivers are included with the installation. But for a lot of hardware, special device drivers are required. If drivers are corrupted or not installed properly, Windows will report a device error. One of the device errors that Windows can report is a “Driver Irql Not Less Or Equal” error. This can result in a blue screen.
The irql not less or equal error basically indicates a problem with the system resources used by a hardware device, such as I/O address ranges, DMA, and IRQs. The IRQ is an interrupt request, which is used by the hardware to claim CPU time from the system. The number of IRQs in a PC however, is limited so sometimes different devices end up sharing an IRQ.
The Driver Irql Not Less Or Equal error can happen in any version of Windows, from Windows XP to Windows 11. The irql error can happen with the NDIS.SYS file, if the error is caused by a network or modem card, but other hardware can also be the cause of the conflict. Because of the severity of this kernel-level problem, the error results in a blue screen or stop error. Driver errors would normally be obvious because the blue screen error lists a .SYS file.
#1 – Using the .SYS filename, you can find out which device or hardware is responsible for the error. You can then disable the hardware in the Windows Device Manager to see if the device is really the cause of the error. If the .SYS filename is not shown on the blue screen, use Event Viewer or a memory dump to find out the responsible driver.
#2 – Running a memory test is also a good idea, as faulty memory can be the cause of many stop errors. In the Bios, disable the quick start, so the full diagnostics are run, and a memory test can be run using the software.
#3 – In most cases, the ‘irql not less or equal’ error can be solved by updating the drivers for the device causing the error. Also make sure you update your Windows and antivirus software, as some of these errors are not caused by hardware, but software problems. You can use the Windows device manager to uninstall any currently installed driver for the device and then reinstall the latest driver. When you reboot your PC after uninstalling the drivers, Windows will detect the new hardware, which allows you to install the latest drivers for the device.
If you do not have the drivers for the device in error or are not comfortable with using the Windows device manager, you can also use a driver update program to find, download, and update all device drivers for you. Driver update software will accurately identify your hardware, including the device in error, and automatically install the latest drivers for it. This can solve driver irql not less or equal errors.
#4 – If updating the drivers does not fix the issue, try loading the default BIOS/UEFI options. This will ensure that RAM timing, FSB timing, and CPU timing are not causing the error. Further, you can check the resource assignments on the devices in the Windows Device Manager to check if there is an IRQ conflict.
#5 – Microsoft further advises that you try to load the last known good configuration using the start menu (press the F8 key during boot). But you do need to make sure that the problem does not introduce itself again as a result of changes or updates. So the best way is to find the real cause of a blue screen error and fix it.
And, for people that are still running Windows 2000, there is another possible cause for the driver_irql_not_less_or_equal error. It is related to dismounting drive volumes. Check the Microsoft knowledge base article on this to fix it.
Although we wrote this article originally with older Windows versions in mind, the error can still occur in the latest Windows versions. The basis approach to solving the error is the same, even for Windows 10 and Windows 11.
All PCs have a number of devices that are connected either permanently or as required. Some of these devices may be fitted as integral parts of the system while others are connected externally. Common to all these devices are device drivers or PC drivers, which act as a link between the operating system and the devices. They interpret operating system commands so that devices can understand them, enabling the operating system to issue high-level commands that take no account of the actual device to which they are connected. One such category is audio drivers.
Most PCs have a dedicated sound card fitted, which provides the audio from your computer, ranging from warning beeps to speech and music. A sound card may also need to handle audio input through a microphone, such as voice input to a dictation application or where voice commands are enabled. It may additionally have to deal with audio input and output together if you have a telephone connected in order to make VOIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) telephone calls.
In some cases, there is no separate sound card and all audio output is handled by a chipset on the computer’s motherboard. This does not give the same quality of sound as a dedicated sound card and audio input are not handled. Every sound card or audio chipset will have a special kind of device driver or PC driver, known as an audio driver, which ensures that the sounds that come out of your computer are as they should be and that input sound is interpreted correctly.
Depending on what you use your computer for, sound may be emitted through a variety of devices — possibly speakers built into the PC’s display screen, dedicated speakers connected to audio ports, or a complete home theatre speaker system. When sound is handled by the motherboard only, output audio will be via internal and limited speakers. You will know if your PC has a sound card fitted because, if it has, there will be marked input and output sockets at the rear of the computer’s case. Here you can plug in headphones, speakers and microphones. If you have a VOIP telephone, this will plug into a USB socket.
Clearly, your PC’s sound card or chipset, and their associated audio drivers, need to be able to handle all the different possibilities.
There are a large number of sound cards and motherboard chipsets available from various manufacturers. Additionally, there are very many devices that can be connected to sound cards and various programs that can input or output through them. This gives a tremendous number of possible combinations that an operating system simply cannot handle.
The answer to the problem is to provide audio drivers for the various cards and devices. These are specific to the device and have versions for particular operating systems. When a sound is to be emitted through a device, the operating system will output the sound and a high-level command that states what is required. This is interpreted by the audio driver so that the command sent to the device is in a form that the device can understand. Similarly, when sound is input, it is sent with a processing request that the audio driver translates before passing it to the operating system.
In addition to solving the problem of multiple sound cards and devices, an audio driver also deals with different sound formats (such as WMA, WAV/PCM, MP3, and FLAC). It may handle playback and recording at the same time if a duplex sound card is fitted, may cover various input and output streams (16-bit, stereo, 48 kHz), and could cater to different formats (such as high-definition audio).

Sometimes audio drivers can cause a problem, which may become apparent when there is poor sound quality. Other possible problems can relate to uncomplete support for surround sound, Dolby/DTS problems, or audio devices not being recognized when connected.
One way to resolve this may be to let Windows reinstall them when you restart the PC. To do this, access Device Manager. Depending on the operating system you use, this may be available from the Control Panel or by right-clicking My Computer and then choosing Manage.
The Device Manager will list the types of devices in the right pane and you need to delete all devices under the “Sound, video, and game controllers” heading, then reboot. If this doesn’t work, update the drivers by re-selecting the device through Device Manager. Click Properties, select the Driver tab, and click the Update Driver button to download drivers and install the latest version on your PC. When you complete the process, restart your computer.
If the sound level is not correct, select Sound in the Control Panel, choose the playback and recording device, and click Properties. Then set the required volume at the Levels tab.
Got Outdated Drivers?
CLICK HERE to Automatically Update and Maintain Your Drivers!
Your PC will have several devices connected, both internal devices such as disk drives and sound cards, and external ones such as printers and scanners. Each of these devices will have a device driver or PC driver that interprets the operating system’s commands so that they can be carried out correctly by the device. Drivers will be installed by Windows, but you can also manually install, update, and roll back drivers.
When you get a new Windows PC, it will have a certain number or device drivers installed and, as you add further devices, you will install device drivers that are supplied with them. Over time, device manufacturers will issue new PC drivers that are designed to fix known problems, improve security or enhance the performance of the device. You should, therefore, download and update drivers frequently to ensure you have up-to-date versions and everything works as it is intended to do.
As with any software, a new version of a device driver can cause problems. It may conflict with something else you have installed or may not work properly for some reason. Because of this, you should always backup drivers before installing new versions so that you can, if necessary, go back to a previous version that worked.
One way to backup drivers is to create a restore point before you update your drivers. This is possible with certain versions of the Windows operating systems, starting with Windows Vista. An alternative is to try to back them up manually but this is fraught with danger since you’ll probably not get them all. They are generally somewhere like C:\Windows\system32\drivers the Device Manager will give you the exact location of each one. The good news is that, if you use Device Manager to update your drivers, it will keep a copy of the old version.
If you start to experience problems after updating a driver or after updating software that may have come with new device drivers, then the driver may well be the cause of the problem. The hardware may refuse to work or may not operate correctly. This may be because it is not compatible with the version of the operating system that you are using.
When you experience problems in these circumstances, the best solution is usually to rollback drivers to their previous versions and see if this cures the fault.
If you have created a restore point, you can simply go back to that point so that you use the device drivers before the update was done. None of your data will be affected by this and you can rollback several PC drivers in one operation. To go back to a restore point, select System Restore from the Control Panel and choose to restore to the latest or a previous restore point.
When you have taken a backup of drivers, you can copy these versions back in place of the updated ones. However, the alternative and much safer method is to rollback your drivers individually, which will identify the driver causing the problem if you have updated several device drivers together. To do this, access Device Manager. Depending on the Windows version you use, this may be available from the Control Panel or by right-clicking My Computer then choosing Manage. Device Manager will list the types of device in the right pane and you need to open up each one to see the actual devices you have connected.
Right click the device and click Properties in the popup menu, then click the Driver tab to see details of the installed device driver.
Click the Roll Back Driver button and then confirm the action to set the driver back to the previous version.
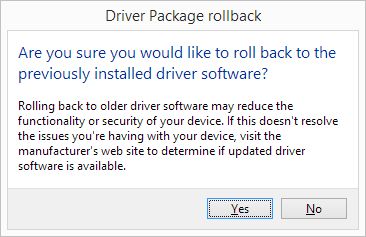
In Newer Windows versions, like Windows 10, the confirmation window has been updated to include a specification of the reason for the rollback.
On completion, you will be prompted to restart your computer. Choose to do this and then check that the fault has been corrected. If not, you may need to rollback other drivers until things are back to normal.
Do keep in mind that later versions of Windows, drivers are automatically updated. So you might need to disable automatic driver updates in Windows 10 to prevent that problematic driver updates get installed again.
 CLICK HERE to Download DriverFinder and check for update Windows Drivers!
CLICK HERE to Download DriverFinder and check for update Windows Drivers!
All computer hardware needs device drivers to communicate with the operating system. In Windows, quite a few device drivers are included with the installation. But for a lot of hardware, special device drivers are required. If drivers are corrupted or not installed properly, Windows will report a device error. One of the device errors that the Windows Device Manager can report is a code 10 error, indicating that the device cannot start.
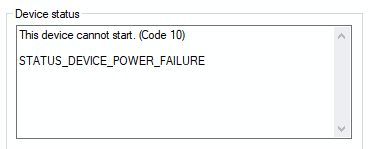
Apart from the main code 10 error message, additional detail under the message can be helpful in identifying the cause. Details can point to insufficient resources or device power issues, but very often you’ll just see “The requested operation was unsuccessful“.
A code 10 error means one of the following:
To fix code 10 errors, the first steps are always to check if your hardware is compatible with your Windows version. Next, make sure your Windows version is up to date with the latest patches and service packs installed. If all this is done, the next step is to update and install your drivers. If code 10 is caused by driver issues, updating the drivers is going to solve it. You can use the Windows device manager to uninstall any currently installed driver for the device and then reinstall the latest driver.
If you do not have the drivers for the device in error, you could try using a device driver update program to find, download and update the drivers for you.
If you are running Windows XP with SP1 or SP2, the error code 10 can also occur for FireWire, or IEEE 1394 devices. In that case, you need to install a hotfix from Microsoft.
If the code 10 error occurs for a DVD driver, there could be a problem with your registry. In most cases, this is the result of installing or uninstalling software for DVD creation or burning, like Nero or Roxio.
The result is a corrupt registry. Sometimes simply uninstalling the CD-burning software helps, but often you also need to delete some registry entries. More specifically the UpperFilters and LowerFilters of the DVD device class. Luckily Microsoft again has a simple solution for this, which includes instructions for manually editing the registry as well as a tool to fix the problematic registry keys.
With external devices, the connection can also be a problem, so make sure you try different ports if possible (especially with USB devices), check or change cables, and remove USB hubs if used. Removing and reinstalling the drivers for all USB controllers can also help in the case of USB devices. Simply uninstall the USB controllers in the Device Manager, restart Windows and let the devices and drivers be reinstalled.
A last possible cause for code 10 errors is that the device has configuration problems. Always try the hardware with the default settings first, and then install the drivers. Configuration errors can also be found in the Device Manager, by checking the resource assignments for the device. Any conflicts between devices can cause one of the devices not to start.
For the latest Windows versions, please also see our article for code 10 errors in Windows 7. Most solutions are the same in later Windows versions.
To understand device drivers, we need to know about devices in the context of personal computers.
Your PC can have lots of devices connected to it. These may be devices that are:
A device driver, sometimes also known as a PC driver, is a means of communication between the PC and a particular device.
It is possible to connect a huge range of devices to a PC – any number of printers, storage devices, and communications equipment. Each of these devices has different requirements and characteristics while your PC’s operating system may also vary, with separate versions of Windows, Linux, and the Mac operating system having different ways of working and a whole range of commands.
The problem is that all the various operating systems need to be able to talk to each device, or at least most of them so that they can be used on the PC. They need to issue requests and receive responses so that everything works. But with so many variations, with literally thousands of devices being available, the permutations and combinations are impossibly high.
The answer to the problem is a device driver, which is developed for a specific device and has versions for the various editions of operating systems. The purpose of the device or PC driver is to serve as a bridge between the PC and a device, interpreting requests from the operating system and passing them to the device, then handling responses from devices in the opposite direction. As a result, the operating system can issue generic commands and receive generic responses, without needing to know or care about the specific device to which it is connected. The operating system only needs to know that is it a laser printer, hard disk or whatever, and can issue high level commands accordingly. The device driver simplifies the whole process.
Most computer processing is concerned with handling data and, depending on the type and use of the data, there are different programs to deal with it. Word processors cover letters and documents, spreadsheets handle data in tabular form, there are drawing applications, video editing products and all kinds of software.
Each of these programs will generally need to communicate with devices, reading data from a disk and outputting a report to a printer, for example. All communications go via the computer’s operating system and device drivers are used to interpret the command so that the device can understand it.
If a database program wants to output a report, it will send the data and print command to the appropriate printer via the operating system. Since the printer has device drivers loaded, the operating system only needs to issue a high level command to the printer without bothering about what type of printer it actually is. The device driver will interpret this command, breaking it down into low level commands that are specific to the printer, before passing them on.
When the printer or other device receives the commands, because they have been interpreted and translated by the device driver, it understands them and can act accordingly. Once the command is successfully completed, or if there are problems, a suitable response is sent back. This response is picked up by the device driver and again interpreted by it, this time converting it from a device-specific command into a high level command that is passed to the operating system and then to the program so that the outcome is known.
Much computer processing involves a whole series of commands and responses being passed backwards and forwards. Each one is picked up and translated by the appropriate device driver so that it is meaningful to the recipient. Device drivers, therefore, have a vital role to play in the smooth operation of a PC.
![]() Got Outdated Drivers?
Got Outdated Drivers?
CLICK HERE to Automatically Update and Maintain Your Drivers!